
Mastering Data Projects: Strategic Consultancy Insights (Part II)
Key Components of Strategic Data Consultancy

Posted by Cesar Alberto Bonilla Magallanes
on January 17, 2025 · 6 mins read
Index
👉 Key Components of Data Consultancy
👉 Project Initiation and Planning
👉 Frameworks and Methodologies
A brief recap
In Part I we spoke about digital transformation, current trends and what the industry demands. We strongly recommend you read part I before tackling this one, because they are part of a series. In this article, we are going to go over key components of Strategic Consultancy, best practices, and technologies.
Key Components of Strategic Data Consultancy
Strategic consultancy plays a vital role in helping organizations drive innovation through the use of data, while enhancing data-driven decision-making, and achieving sustainable growth.
As businesses increasingly rely on data-driven insights, the demand for strategic consultancy skyrockets. This involves aligning business goals with technical capabilities, managing stakeholder relationships, ensuring compliance with regulations, and adopting cutting-edge technologies.
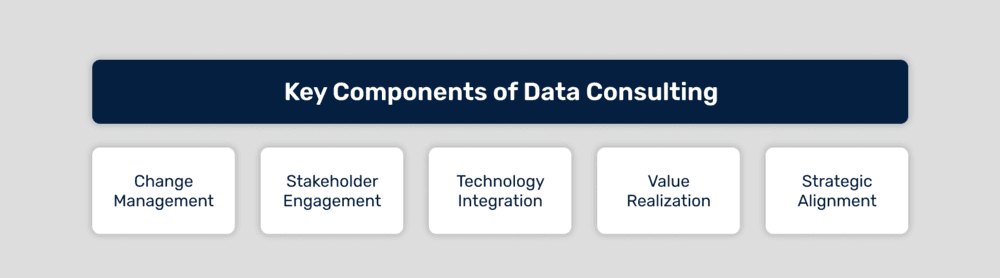
By focusing on key components such as strategic alignment, stakeholder engagement, value realization, change management, and technology integration, strategic consultants can guide organizations in transforming their data projects into impactful initiatives that deliver measurable value.
Business Components
Strategic Alignment Ensuring data projects align with overall business goals and strategies. This involves understanding the organization's vision, mission, and objectives to guide project planning and execution. This seems trivial but requires a lot of capacity to gain information from less interactions with important stakeholders inside the organizations because they are usually busy, and find out resources from where to get alignment, like Company Values, Goals, Trends, latest product/services presentations and so on.
Stakeholder Engagement Effectively managing and communicating with stakeholders to ensure their needs and expectations are met. This includes regular updates, feedback loops, and alignment meetings. This is a cornerstone to achieving successful goals in data projects because there is a constant translation from data results to business that would require superior communication skills. Humanizing Data Strategy book author, Tiankai Feng proposes an interesting way to follow with his 5Cs Framework (Competence, Communication, Collaboration, Creativity, Conscience).
Value Realization Focusing on delivering measurable results from data projects to drive business value. This involves defining key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to track and demonstrate the impact of data initiatives.

Change Management Addressing the organizational change required to adopt new data-driven processes and technologies. This includes training, communication, and support to ensure smooth transitions. Patil and Hilary Mason in their book Data Driven: Creating a Data Culture (2014), mention how organizations could start adopting how to address change like software development and devops, and how this could bring important improvements in thriving throughout the organization's goals.

Governance and Compliance Implementing data governance frameworks to ensure data quality, privacy, and security. This includes adherence to regulatory requirements and industry standards. Companies struggling with the bigger picture of their data assets and platforms require more efforts to address changes and incremental improvements. Helping organizations overcome these issues provides an intrinsic value and an open opportunity for new projects.
Technical Components
-
Data Engineering: Building and maintaining the infrastructure to collect, store, and process data. This includes data pipelines, ETL (or ELT) processes, and data lake/warehousing solutions.
-
Data Architecture: Designing a scalable and robust architecture for data storage and retrieval. This involves choosing appropriate databases, data models, and technologies to support data accessibility and performance. The right selection of this collection of tools and combination of pieces avoids inconsistencies and unnecessary spending; mostly these issues result from a lack of vision to scale up while the company is growing.
-
Data Science, Machine Learning, and AI: Developing and deploying machine learning models to extract insights and automate processes. This includes model selection, training, validation, and deployment, as well as ongoing monitoring and maintenance. The goal is analyzing and interpreting complex data to provide businesses with digestible information to make informed decisions. This involves statistical analysis, data visualization, and the development of predictive and prescriptive models.
-
Technology Integration: Ensuring seamless integration of various data tools and technologies within the existing IT ecosystem. This includes APIs, data integration platforms, and middleware solutions.
What happens when you don't handle those components?
The business impact and the client’s satisfaction are going to be in jeopardy. The engagement is the most important thing to care about, not focusing on the human aspects would result in problematic consultancy experiences that would put the role of a strategic partner in the worst position. Not having tech skills or a team prepared to face some challenges, would result in also poor performance of the engagements and then put the role of a strategic partner in the wrong spot.
Strategic Approaches
A strategic approach to strategic consulting for data projects is a thoughtfully designed plan that guides how an organization builds and implements data systems to achieve its business objectives.
This approach involves carefully considering the alignment of data initiatives with business goals.
Adopting the following items, data projects can align with business objectives, utilize the right technologies, and deliver value effectively.
Project Initiation and Planning
-
Requirement Gathering: Collecting detailed requirements through interviews, surveys, and workshops to understand stakeholder needs.
Mutt Data is a technology company that helps startups and natively digital businesses to develop and implement machine learning and artificial intelligence solutions that generate actual and impactful results in business. We have several Cloud Provider competencies including AWS Advanced consulting partners and we are the only ones in the SOLA region that have earned the AWS Advertising and Marketing Technology Competency. -
Stakeholder Alignment: This is vital. Regular communication and meetings to ensure all stakeholders agree on project goals, scope, and deliverables.
-
Project Scoping: Defining project deliverables, timelines, and resources in a detailed project plan.
Frameworks and Methodologies
-
CRISP-DM: A six-phase methodology for data projects: business understanding, data understanding, data preparation, modeling, evaluation, and deployment.
-
Agile: An iterative approach emphasizing flexibility, collaboration, and quick delivery using methods like Scrum and Kanban.
-
Lean: A focus on maximizing value and minimizing waste to streamline processes and improve efficiency.
Mutt Data is a technology company that helps startups and natively digital businesses to develop and implement machine learning and artificial intelligence solutions that generate actual and impactful results in business. We have several Cloud Provider competencies including AWS Advanced consulting partners and we are the only ones in the SOLA region that have earned the AWS Advertising and Marketing Technology Competency.
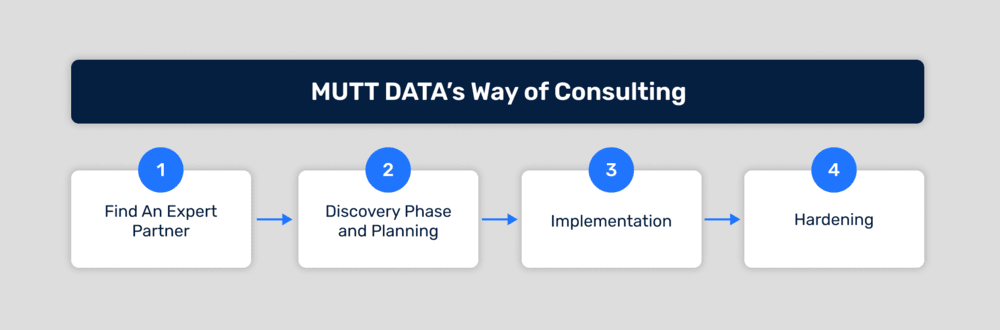
At Mutt Data, we like to do things comprehensively. That is why we recommend:
-
Find an expert partner: someone who knows what they are doing (cursive) and that has a proven track record on the subject matter. Demonstrating vision beyond current issues, also would be a good sign of a great partner. For example, we strive to create a strategy based on data and we enjoy it.
-
Do a Discovery phase & then some planning: Take the time to understand your current technology and business context and identify your data tooling and capability maturity. This implies understanding the context, the technology, the business maturity, if there's technical debt, the data architecture, the main stakeholders and the business as a whole. Then, establish SMART goals. Which are measurable, feasible, reasonable goals, in order to determine how you will solve the problem or problems you detected during discovery.
-
Implementing: Once you have completed the discovery phase, then hands on solving and building the solutions. Keep an eye on unforeseen challenges and adapt to reach the best outcome.
-
Hardening: Hardening: Implementing different monitoring, reporting, and control variables to your system is always up to date. In the middle, we prepare, teach and evangelize teams to adopt the solutions. This phase is quite important to define processes that maintain the solutions implemented, so spreading the knowledge and how to handle things would guarantee the life of the value delivered.
Technology Selection
Usually takes place in the discovery phase, and sometimes could be revisited during the implementation phase, when facing some challenges or new ways to solve problems arise.
-
Tool and Platform Evaluation: Assessing tools and platforms based on scalability, ease of use, and integration capabilities, and conducting proof-of-concept tests.
-
Cloud vs. On-Premises: Choosing between cloud-based and on-premises solutions based on cost, security, and scalability needs. We even consider hybrid approaches.
-
Data Integration: Ensuring seamless integration of various data sources using ETL/ELT tools, integration platforms, and APIs.
Best Practices
-
Iterative Development: Breaking the project into smaller, manageable chunks for regular feedback, testing, and adjustments.
-
Collaboration and Communication: Promoting teamwork and regular updates to keep everyone aligned.
-
Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating potential risks through ongoing assessments and strategies.
-
Documentation: Ensuring clear documentation of processes and conceptualization of the solution.
-
Presentation of Results: Presenting findings and results effectively to lay strong foundations for the project's success.
Follow us on LinkedIn and stay tuned for part III!